The modern food industry is undergoing a rapid transformation, driven by changing consumer expectations, the rise of delivery services, and the need for more agile, cost-effective business models. One of the most impactful innovations emerging from this shift is the ghost kitchen, a delivery-only food production space that eliminates the overhead of traditional brick-and-mortar restaurants. This model has opened up unprecedented opportunities for culinary entrepreneurs, particularly those focused on small batch food production.
From understanding the fundamentals of small batch systems to choosing the right kitchen layout and leveraging technology, this resource will equip you with the tools to create a highly efficient, profitable food business ready for today's on-demand economy.
Understanding small batch production
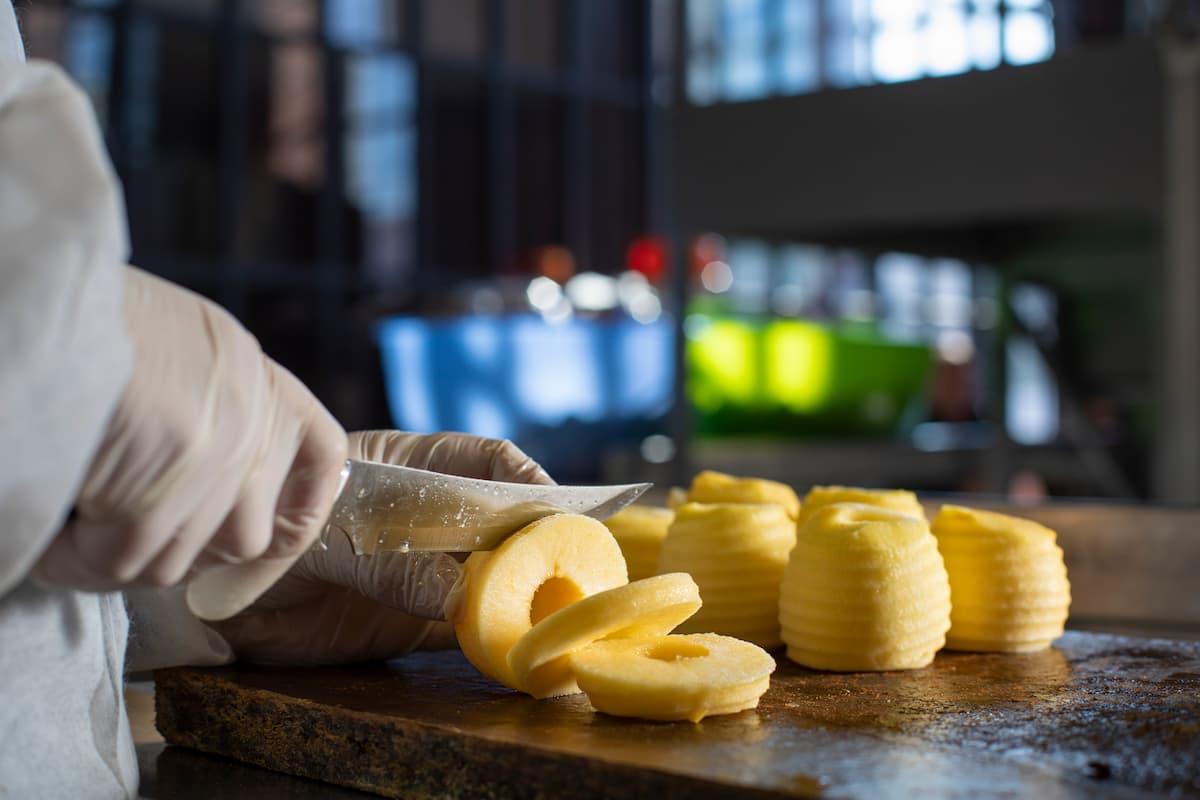
A small batch production refers to the manufacturing of food products in limited quantities, typically tailored to meet specific demand rather than large-scale volume. Unlike mass production models that prioritize scale and cost-cutting, small batch operations focus on customization, quality, and responsiveness to market trends.
In the food industry, this often means preparing food in pre-planned quantities, be it 50 artisan sandwiches or 100 containers of organic soup, rather than producing thousands of units at once.
The appeal of small batch production is its adaptability. Operators can adjust recipes, respond to seasonal ingredients, test new product lines, or meet localized consumer preferences without committing to mass quantities. This model is particularly well-suited for ghost kitchens, which thrive on lean, efficient operations designed for delivery-only channels.
Read more: Best partnerships and services to grow your restaurant’s food delivery success
Benefits of small batch production
1. Flexibility to adapt and innovate
Small batch production allows businesses to pivot quickly. Whether you’re reacting to a viral TikTok food trend or experimenting with a new vegan recipe, producing in smaller quantities enables fast testing and iteration.
2. Greater control over quality
Maintaining consistency and high quality is much easier with small runs. When you're not overwhelmed by volume, you can focus on sourcing premium ingredients, perfecting preparation techniques, and ensuring each product meets your brand’s standards. This leads to better customer experiences and stronger brand loyalty.
3. Inventory and cost efficiency
By producing food in smaller volumes based on actual or forecasted demand, businesses can significantly reduce food waste and spoilage. You buy what you need, cook what you need, and store less, freeing up valuable kitchen space and cash flow. For startups or niche operators, this lean approach to inventory is a major advantage.
4. Lower barriers to entry
Large-scale food production often requires substantial capital investment in specialized equipment, facilities, and staff. In contrast, small batch production, especially when done in a ghost kitchen, can be launched with significantly lower upfront costs.
5. Improved traceability and compliance
Because the production process is more contained and controlled, it becomes easier to track ingredient sourcing, monitor handling practices, and comply with food safety standards. This is particularly beneficial for businesses working with perishable items, specialty diets (gluten-free, keto, allergen-free), or regulated products.
6. Enhanced customer engagement
Small batch production naturally lends itself to storytelling. Customers are drawn to limited releases, locally-sourced ingredients, and handcrafted experiences. Marketing your brand around these attributes helps build a more emotional connection with your audience, turning occasional buyers into loyal fans.
According to research from Unleashed Software, businesses using small batch manufacturing are able to cut inventory holding costs by up to 30% and reduce product obsolescence risk by reacting faster to changes in customer preferences. This efficiency makes it especially attractive to startups or growing businesses that need to stay agile.
Read more: Essential Guide to Industrial Kitchen Equipment for Ghost Kitchens
Examples of batch production in the food industry
Batch production is widely used across various food sectors, particularly in businesses that prioritize quality, consistency, and customization. Below are some common and practical examples where this model is especially effective:
Baked goods
Artisan bakeries and pastry shops often rely on batch production to prepare specific quantities of products like sourdough loaves, croissants, muffins, or seasonal treats. This allows them to maintain high-quality control, adjust for customer preferences, and avoid overproduction. For instance, a bakery may bake 100 chocolate chip cookies in the morning batch and switch to 75 cinnamon rolls in the afternoon, depending on demand.
Sauces and condiments
Small-scale producers of specialty sauces, such as hot sauces, aiolis, chutneys, or dressings, commonly use batch production to test flavors and scale based on market reception. It’s a preferred approach for limited-edition flavors or artisanal products that emphasize handcrafted quality and unique ingredient profiles. This also helps manage shelf-life concerns with perishable ingredients.
Ready-to-eat meals
Ghost kitchens and meal prep services often prepare batches of meals such as pasta dishes, grain bowls, or soups based on weekly menus. A company might prep 250 servings of a chicken teriyaki bowl in a Monday morning batch, then prepare 200 quinoa salads in the afternoon. This approach keeps operations lean, allows for tight inventory control, and aligns with rotating menus.
Beverages
Batch production is also used in small beverage operations, like cold-pressed juices, smoothies, kombucha, and craft teas. Operators can easily adjust recipes for new blends or seasonal offerings. This model is ideal for beverage brands that emphasize freshness and customization.
Frozen meals and niche dietary foods
Businesses producing gluten-free, keto, vegan, or allergen-sensitive foods typically favor batch production to meet strict dietary standards and prevent cross-contamination. For instance, a gluten-free lasagna may be prepared in isolated batches, using dedicated equipment and storage, to ensure regulatory compliance and build trust with health-conscious consumers.
Food trucks and catering services
These operators often prep specific items in batches before heading out to events or service areas. A taco truck might cook and portion 200 servings of carnitas tacos in a morning shift, ensuring they have exactly what they need for the day’s service without waste.
Read more: Frozen food meals: a healthy option for your delivery business
Ghost kitchen layout design for small batch efficiency
Designing an effective layout is crucial for any ghost kitchen operation, especially when focusing on small batch production. Since these businesses prioritize flexibility, efficiency, and product consistency, the kitchen layout must support streamlined workflows, quick changeovers between batches, and optimal use of limited space.
Below are key layout considerations and popular configurations tailored for small batch production environments:
Workstation zoning
Dividing your kitchen into dedicated work zones ensures a logical flow of ingredients and personnel. Common zones include:
- Prep area: Where ingredients are washed, cut, and portioned.
- Cooking area: Includes ovens, stoves, fryers, or sous-vide machines.
- Assembly/plating zone: For combining components into finished products.
- Packaging/shipping area: Equipped with sealing machines, labels, and staging shelves for delivery orders.
By physically separating these activities, ghost kitchens reduce cross-contamination and increase productivity, especially important when managing diverse small batches of meals or SKUs.
Read more: How ghost kitchens are revolutionizing the wellness food movement
Linear or assembly line layout
For kitchens focused on high-efficiency small batch prep, a linear or assembly line setup works well. Ingredients move in a straight path from prep to cook to package. This approach is ideal for standardized menus like grain bowls, burritos, or meal kits. Staff can be trained to handle specific stages, reducing training costs and minimizing bottlenecks during peak times.
Island layout for modular flexibility
The island layout centers around one primary worktable or cooking station with surrounding equipment and storage. This model is useful when producing varied items in small batches, as it supports multi-functional workflows. It’s especially effective in ghost kitchens offering multiple brands or rotating menus, allowing for quick reconfiguration as production needs change.
Galley layout for tight spaces
For kitchens operating in narrow or constrained environments, such as in urban ghost kitchen facilities, the galley layout positions all key stations along two facing walls. This maximizes limited square footage while ensuring that employees have everything within arm’s reach. Small teams can operate efficiently with minimal movement, which is essential when producing custom or niche small batches.
U-shaped layout for ergonomic flow
The U-shaped or horseshoe layout places prep, cook, and packaging stations in a tight triangle, minimizing unnecessary movement. This layout is particularly effective for solo operations or two-person teams producing low-volume, high-quality batches. It enhances control over each production phase and can reduce food handling errors.
Storage and cold-chain integration
For small batch kitchens handling sensitive ingredients (e.g., dairy, fresh produce, or meats), cold storage must be tightly integrated into the layout. Walk-in coolers or under-counter refrigeration units should be located close to prep zones. Dry storage should be clearly labeled and accessible without interrupting workflow.
Scalability and multi-brand considerations
Ghost kitchens often host multiple virtual brands. When designing for small batch production across brands, consider modular setups, like rolling carts for mobile storage, color-coded containers to reduce cross-contamination, and flexible workstations that can adapt to different equipment needs (e.g., grill for one brand, steamer for another).
Safety and compliance
Ensure that your layout adheres to local health codes and safety regulations. This includes proper ventilation, fire suppression systems, handwashing sinks, and sanitation stations. A safe and compliant layout is essential for passing inspections and maintaining customer trust.
Kitchen design software like SmartDraw or The Kitchen Planner can help simulate workflows and test different layout configurations before investing in equipment. This can save time and reduce costly design errors that might hinder batch productivity later on.
In summary, your ghost kitchen’s physical layout should support flexibility, speed, safety, and clear workflows. Whether you're producing 50 keto bowls or 200 vegan pasta dishes, a well-designed space enables small batch efficiency and helps your business scale sustainably.
Read more: How Ghost Kitchens can boost your restaurant’s profitability
How CloudKitchens empowers small batch production success
If you're ready to bring your small batch food business to life or scale an existing concept without the burden of building a facility from scratch, CloudKitchens offers a powerful solution.
With fully equipped, ready-to-use kitchen spaces in strategic locations, food entrepreneurs can streamline production, tap into high-demand delivery zones, and benefit from integrated operational support, covering everything from logistics to marketing tools.
This flexibility and infrastructure make it easier to maintain quality, manage costs, and grow your brand. Whether you're launching a niche meal prep service or scaling a local favorite, CloudKitchens gives you the foundation to succeed. Ready to turn your food concept into a thriving business? Discover how CloudKitchens can help you get started today!
DISCLAIMER: This information is provided for general informational purposes only and the content does not constitute an endorsement. CloudKitchens does not warrant the accuracy or completeness of any information, text, images/graphics, links, or other content contained within the blog content. We recommend that you consult with financial, legal, and business professionals for advice specific to your situation.